23 Graded Potentials
Local changes in the membrane potential are called graded potentials and are usually associated with the dendrites of a neuron. The amount of change in the membrane potential is determined by the size of the stimulus that causes it. In the example of testing the temperature of the shower, slightly warm water would only initiate a small change in a thermoreceptor, whereas hot water would cause a large amount of change in the membrane potential.
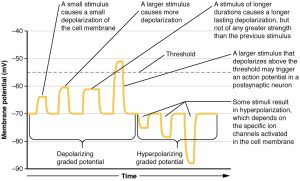
Graded potentials can be of two sorts, either they are depolarizing or hyperpolarizing. For a membrane at the resting potential, a graded potential represents a change in that voltage either above -70 mV or below -70 mV. Depolarizing graded potentials are often the result of Na+ or Ca2+ entering the cell. Both of these ions have higher concentrations outside the cell than inside; because they have a positive charge, they will move into the cell causing it to become less negative relative to the outside. Hyperpolarizing graded potentials can be caused by K+ leaving the cell or Cl– entering the cell. If a positive charge moves out of a cell, the cell becomes more negative; if a negative charge enters the cell, the same thing happens.
(https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/12-5-communication-between-neurons)
Types of Graded Potentials
For the unipolar cells of sensory neurons—both those with free nerve endings and those within encapsulations—graded potentials develop in the dendrites that influence the generation of an action potential in the axon of the same cell. This is called a generator potential. For other sensory receptor cells, such as taste cells or photoreceptors of the retina, graded potentials in their membranes result in the release of neurotransmitters at synapses with sensory neurons. This is called a receptor potential.
A postsynaptic potential (PSP) is the graded potential in the dendrites of a neuron that is receiving synapses from other cells. Postsynaptic potentials can be depolarizing or hyperpolarizing. Depolarization in a postsynaptic potential is called an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) because it causes the membrane potential to move toward threshold. Hyperpolarization in a postsynaptic potential is an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) because it causes the membrane potential to move away from threshold.
Summation
All types of graded potentials will result in small changes of either depolarization or hyperpolarization in the voltage of a membrane. These changes can lead to the neuron reaching threshold if the changes add together, or summate. If the total change in voltage in the membrane is a positive 15 mV, meaning that the membrane depolarizes from -70 mV to -55 mV, then the graded potentials will result in the membrane reaching threshold.
For receptor potentials, threshold is not a factor because the change in membrane potential for receptor cells directly causes neurotransmitter release. However, generator potentials can initiate action potentials in the sensory neuron axon, and postsynaptic potentials can initiate an action potential in the axon of other neurons. Graded potentials summate at a specific location at the beginning of the axon to initiate the action potential, namely the initial segment. For sensory neurons, which do not have a cell body between the dendrites and the axon, the initial segment is directly adjacent to the dendritic endings. For all other neurons, the axon hillock is essentially the initial segment of the axon, and it is where summation takes place. These locations have a high density of voltage-gated Na+ channels that initiate the depolarizing phase of the action potential.
Summation can be spatial or temporal, meaning it can be the result of multiple graded potentials at different locations on the neuron, or all at the same place but separated in time. Spatial summation is related to associating the activity of multiple inputs to a neuron with each other. Temporal summation is the relationship of multiple action potentials from a single cell resulting in a significant change in the membrane potential. Spatial and temporal summation can act together, as well.
Media Attributions
- 5bb704dbd33867c5cf2af64de357e682ce789fc3

